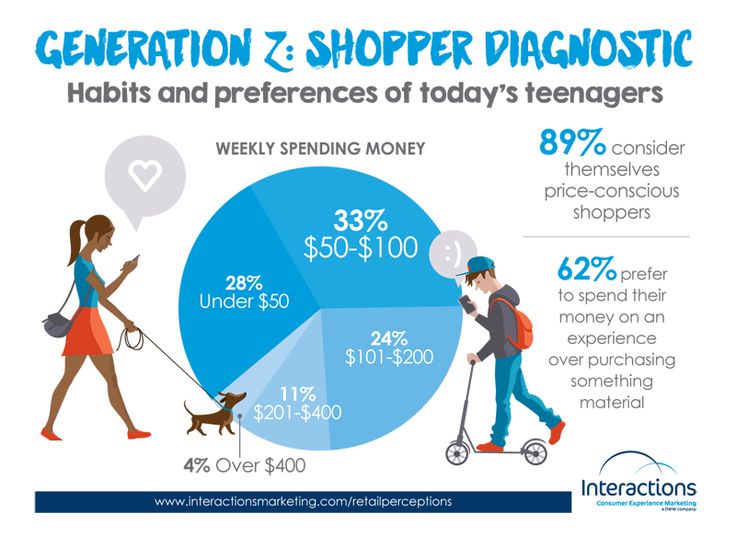
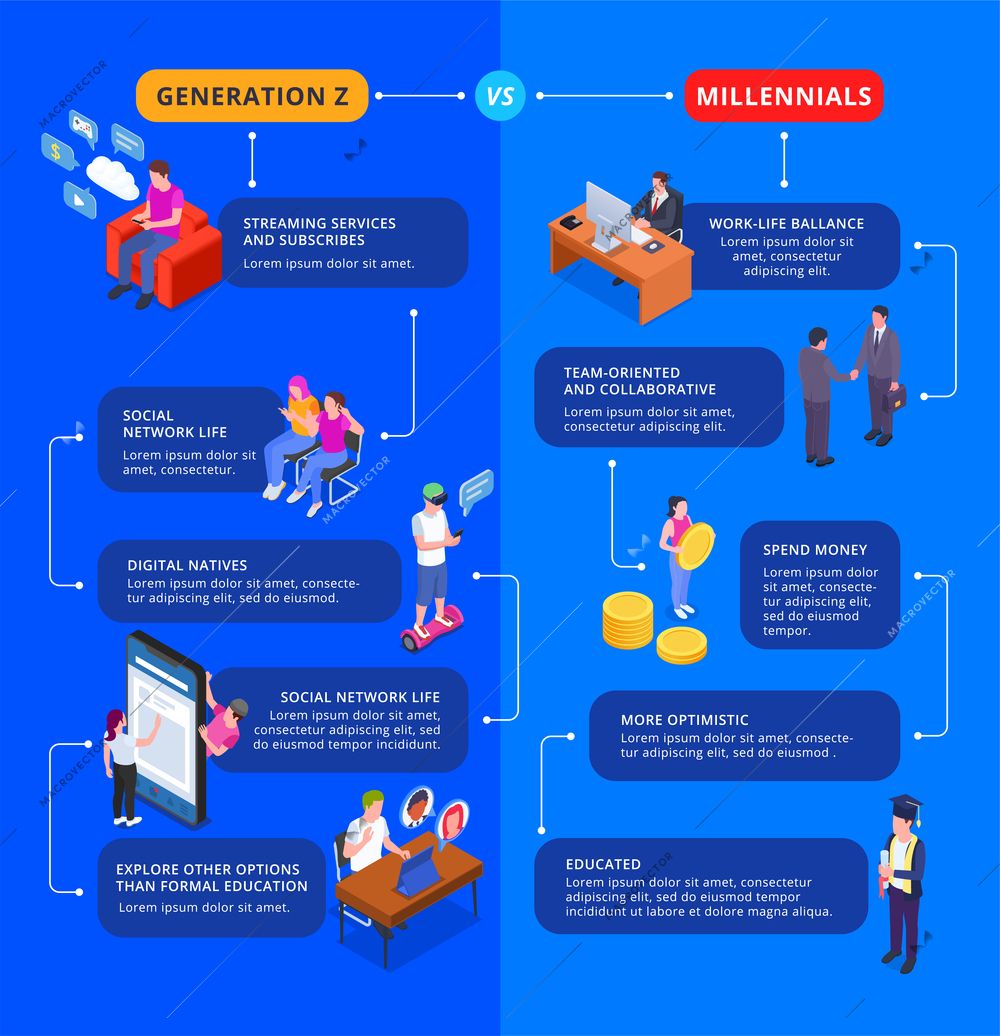
The financial world is undergoing a transformation, and at the heart of this change is Generation Z. Born between the late 1990s and the early 2010s, this generation has entered adulthood in an era defined by digital innovation, economic uncertainty, and a rapidly shifting job market. Unlike Millennials who experienced the dot-com boom and financial crises during formative years, Gen Z has come of age during global challenges such as the COVID-19 pandemic, climate change concerns, and rising inflation. These unique experiences shape how they earn, save, invest, and spend money.
This article explores in depth how Gen Z is rewriting financial habits, why their approach differs from earlier generations, the tools and platforms they use, and what businesses, financial institutions, and policymakers can learn from their behaviors.
Understanding the Gen Z Mindset Toward Money
Gen Z’s relationship with money is heavily influenced by the digital environment they grew up in. Unlike previous generations, their habits are shaped by instant access to information, online financial education, and exposure to both opportunities and risks of the digital economy.
A. Pragmatic and Cautious
Witnessing global recessions and market instability during their youth has made Gen Z cautious about financial risks. Many of them prefer to research thoroughly before making decisions.
B. Digitally Informed
Thanks to YouTube tutorials, TikTok finance creators, and free investment apps, Gen Z is one of the most financially educated generations at an early age. Financial literacy content is often consumed casually alongside entertainment.
C. Purpose-Driven Spending
Values like sustainability, diversity, and social responsibility influence how they spend money. They are more likely to support ethical brands and avoid companies involved in environmental or social controversies.
D. Balancing Security and Flexibility
Unlike Boomers who sought stable 9-to-5 jobs and pensions, Gen Z is interested in balancing job security with side hustles, freelancing, and entrepreneurial ventures. This balance creates financial habits that differ significantly from past norms.
Key Financial Habits of Gen Z
Gen Z’s financial behaviors reflect a mix of caution, digital literacy, and creativity. Below are the defining habits reshaping the financial world.
A. Embracing Digital Banking
Traditional brick-and-mortar banking is no longer the default. Gen Z prefers digital banks and mobile-first platforms that offer:
User-friendly apps
Instant transfers
Budgeting tools integrated into accounts
Low or no fees
Neo-banks and fintech platforms like Revolut, Chime, and Monzo have become popular choices for their transparency and convenience.
B. Prioritizing Financial Education
Gen Z actively seeks financial knowledge from online communities. TikTok’s “FinTok” has millions of views where creators simplify topics like investing, budgeting, and credit management. Unlike older generations who relied on professional advisors, Gen Z crowdsources knowledge from peers and influencers.
C. Side Hustles and Multiple Income Streams
The gig economy is a significant part of Gen Z’s financial reality. Many juggle freelance work, online businesses, and content creation alongside traditional jobs. Platforms like Fiverr, Upwork, and Etsy allow them to diversify income.
D. Investing Early and Diversely
Unlike Millennials, who often delayed investing, Gen Z starts early. They use apps like Robinhood, eToro, and Coinbase to experiment with:
Stocks
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs)
Cryptocurrency
Fractional shares
This diversification shows a willingness to take risks while also learning by doing.
E. Focus on Credit and Debt Management
Gen Z is cautious about falling into debt traps. They use credit monitoring apps, prepaid debit cards, and budgeting tools to avoid mistakes common to Millennials during their early financial years.
F. Conscious Consumerism
Purchasing decisions reflect personal ethics. Gen Z prefers second-hand clothing, eco-friendly packaging, and transparent supply chains. They are driving the popularity of thrift shopping apps like Depop and Vinted.
How Technology Shapes Gen Z’s Financial World
Technology is at the core of Gen Z’s financial behavior.
A. Mobile-First Banking
Financial institutions have had to redesign apps to meet Gen Z’s expectations for sleek interfaces, real-time notifications, and customizable dashboards.
B. Digital Wallets and Contactless Payments
Platforms like Apple Pay, Google Pay, and PayPal are standard. For Gen Z, carrying physical cash or even cards feels outdated.
C. Crypto and Blockchain
Despite volatility, cryptocurrencies attract Gen Z due to decentralization and innovation. NFTs and blockchain-based assets also gained popularity, especially during the 2020–2021 boom.
D. Social Finance Platforms
Apps like Venmo or Cash App make splitting bills and sending money to friends seamless. These tools turn financial transactions into a social activity.
Gen Z’s Challenges with Money
Although Gen Z shows maturity in some areas, they also face unique challenges that affect their financial journey.
A. High Cost of Living
Rising housing prices, student debt, and inflation make saving and investing harder.
B. Job Market Instability
Automation, layoffs, and contract-based work leave Gen Z feeling financially insecure, driving their interest in side hustles.
C. Financial Overload Online
While financial content is easily accessible, not all advice is reliable. Many fall prey to scams or risky investment tips from unverified sources.
D. Mental Health and Money Stress
Gen Z is more open about mental health, but financial stress remains a common concern. Balancing aspirations with financial reality creates pressure.
The Role of Social Media in Gen Z Finance
Social media plays a powerful role in shaping financial behavior.
A. Financial Influencers
“Finfluencers” create bite-sized lessons on budgeting, credit scores, and investing. Their relatable style resonates with Gen Z far more than traditional advisors.
B. Community Learning
Online forums like Reddit’s r/wallstreetbets or r/personalfinance act as educational spaces where young people exchange knowledge.
C. Virality of Trends
Meme stocks, crypto booms, and TikTok money hacks show how viral trends influence real financial decisions, sometimes with mixed results.
The Future of Gen Z Financial Habits
Looking forward, Gen Z’s financial practices are likely to become even more influential as they grow older and gain higher incomes.
A. Integration of AI in Personal Finance
AI-driven financial planning tools will provide Gen Z with customized savings and investment strategies.
B. Expansion of Green Finance
Sustainable investments, renewable energy stocks, and ethical funds will become a norm.
C. Rise of Digital-First Financial Ecosystems
Banks and fintech companies will compete to provide everything—banking, insurance, investing, and payments—within one seamless app.
D. Global Freelance Economy
With remote work normalized, Gen Z will continue leveraging global platforms for income, diversifying far beyond local opportunities.
Conclusion
Gen Z’s financial habits are reshaping the global economy. With a mix of caution, creativity, and digital fluency, they are breaking away from traditional financial systems and creating a more dynamic approach to money. Their values-driven consumerism, interest in early investing, and reliance on digital platforms represent not just generational quirks but long-term transformations.
For businesses, financial institutions, and policymakers, understanding Gen Z’s habits is not optional—it is essential. Those who adapt to their expectations of transparency, inclusivity, and digital convenience will thrive in the years to come.
Gen Z is not waiting to inherit the financial future; they are actively building it right now.